The burden on the food supply is increasing as population growth is expanding quickly. In turn, this causes a rise in food insecurity and additional greenhouse gas emissions and extensive environmental damage. So, food production must develop to suit both a growing population and the changing environment. The current population of the World in 2023 is 8,045,311,447, a 0.88% increase from 2022.
China (1.4 billion) and India (1.3 billion) remain the two most populous countries of the world, both with more than 1 billion people, each, representing nearly 18 percent of the world’s population respectively. By the end of 2023, India is projected to overtake China as the world’s most populous country, while China’s population is projected to decrease by 48 million, or around 2.7 percent, between 2019 and 2050.
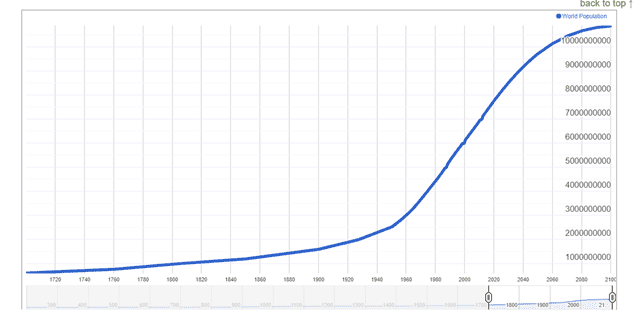
According to The United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UN DESA), the projected population will keep growing, estimates have put the total population at 8.6 billion by mid-2030, 9.8 billion by mid-2050, and 11.2 billion by 2100. We are growing concerning resources, education, and energy, yet demand is rapidly increasing. Modern agriculture is not ready to meet this growing need, as it already faces several difficulties.
Population growth indicates increased food consumption, which raises the need for food production. And the environmental effects of excessive food production are unsustainable such as climate change, soil health degradation, and a sharp decline in the amount of arable land. The overexploitation, intensive farming, and land fragmentation caused by population increase result in a decrease in the quantity and quality of natural resources. Additionally, increasing urbanization leads to deforestation, and it brutally affects agriculture on a large scale.
Many effects of human population expansion on the planet include:
● Increase in the environmental resources being extracted. These resources include minerals, plants, water, and wildlife, particularly in the oceans, as well as fossil fuels (oil, gas, and coal). In turn, the removal of resources frequently results in the release of trash and toxins that degrade the quality of the air and water and endangers the health of both humans and other species.
● Increase in the use of freshwater for drinking, agriculture, recreation, and industrial activities is on the rise. Lakes, rivers, the earth, and artificial reservoirs are all sources of freshwater.
● To build urban areas, including homes, shops, and highways to accommodate expanding populations, forests, and other habitats that are uprooted or destroyed. In addition, when populations rise, more land is used for farming, including raising crops and caring for animals. This in turn has the potential to reduce species populations, geographic ranges, and biodiversity, it also changes how organisms interact with one another.
● Lesser meat is available for consumption by smaller predators which would normally subsist off pre-existing stockpiles from previous years when human population numbers were lower. This has a detrimental impact on other animals' survival rates.
Along with these above-mentioned effects, the population boom directly or indirectly affects the foundation of living – Agriculture. Any particular economy's entire existence depends on agriculture. The foundation of any nation's economic structure is its agriculture. Also, a large number of people can find work in the field of agriculture, in addition to receiving food and raw materials.
Food security for any country is ensured by a stable agricultural industry. Food security is the most important prerequisite for every nation. Malnourishment, which has historically been seen as one of the main issues facing developing nations, is prevented by food security. The primary source of income for most nations is agriculture and its supporting businesses.
Here are some ways agriculture can adapt to feed the world's rising population-
⮚ Reduce Food Wastage- Reducing food waste is the first step in feeding a growing population. In the U.S., between 30 and 40 % of the food produced for human consumption is wasted, around the same percentage that is wasted worldwide. Fortunately, there are numerous approaches to reducing food waste. Using leftover meals as compost or fertilizer is one of the additional techniques to reduce food waste. Likewise, items that are about to spoil might be sold for a reduced price. Moreover, animals can eat meal scraps.
⮚ Conserve Water- Water conservation is critical to feed the world's rising population. Fresh water is becoming increasingly scarce in various parts of the world, including Sub-Saharan Africa, Northern Africa, and Western Asia. Agriculture consumes over 80% of the world's freshwater resources. Agriculture can use less and generate more food if it is managed properly. Several farmers already employ drip irrigation. Pipes are inserted near plant roots in this approach. The pipes carry water and include small holes to allow water to fall onto the roots, allowing the roots to be watered without significant evaporation. Farmers should also use organic fertilizers and mulch to reduce water pollution and retain moisture. Farmers can also construct rain barrels, which are containers that collect rain, on smaller farms. They can then put that to use.
⮚ Maintain Quality of Soils- Another agricultural development to feed a growing population is maintaining good soil health. Soil degradation has an impact on crops because, without soil, much of the products required to feed humans cannot be cultivated. That is why soil protection is essential for good crops. Here are a few examples:
▪ Reduce tillage to disturb the soil as little as possible.
▪ Plant a variety of plants to promote soil microbial biodiversity.
▪ Utilize cover crops, which are off-season crops that help prevent erosion and promote soil health.
▪ To add nutrients and keep the soil moist, cover it with mulch and compost.
⮚ Boost Crop Yields- Although it appears obvious, increasing crop yields is easier said than done. Yet, current advancements in the farming business have been able to accomplish this. Crop yields can be increased through urban agriculture, vertical farming, and sustainable ways. Urban agriculture and vertical farming, which are agricultural systems that use vertical buildings in densely populated regions to raise crops, go hand in hand. They boost agricultural yields without increasing farming acreage. These are farms that cultivate vegetables in vertical buildings, often using hydroponics. Composting, regenerative farming, and soil health maintenance can all be employed on large-scale farms to boost crop yield.
⮚ Make Use of Robots- Robots are possibly one of the most significant agricultural advances. Agriculture robot use has increased and is anticipated to increase by 24.1% until 2024. It gives farmers more time to operate their businesses and develop innovative technology to help feed the world's population. Without robots, farmers would spend hours in the fields sitting on a tractor. Instead, robots can perform monotonous tasks such as weeding, gathering fresh produce, and monitoring agriculture.
