Cattle Ranching is the practice of running a huge farm and raising and breeding herds of grazing livestock such as Sheep and cattle on a large scale. In addition, some also raise beef and dairy cattle, pigs, goats, horses, mules, asses, buffalo, and camels. A Ranch is a large area on which animals are kept.
History of Ranching
People raised livestock throughout the ages but that was not at a large scale or in large areas. The Idea of raising and herding animals started in Spain and Portugal around 1000 CE.
Ranching in the western United States derives from vaquero culture. Ranchers in the USA roam with their cattle and sheep for grazing in an open area owned by the government and then the problem of overgrazing was an issue as the land became degraded. During the winter of 1886-87, Hundreds of 1000 weakened cattle were killed due to the problem of insufficient grazing. Afterward, Ranchers started fencing off their lands and leased lands from the government to limit access to grazing land.
United States- Cattle Ranching Industry
The most important industry in the agriculture sector is Cattle production which contributes the largest share of total cash receipts for agriculture receipts in the economy. The United States has a vast beef industry which is separate from its dairy sector. In addition to having the world's largest fed-cattle industry, the United States is also the world's largest consumer of beef.
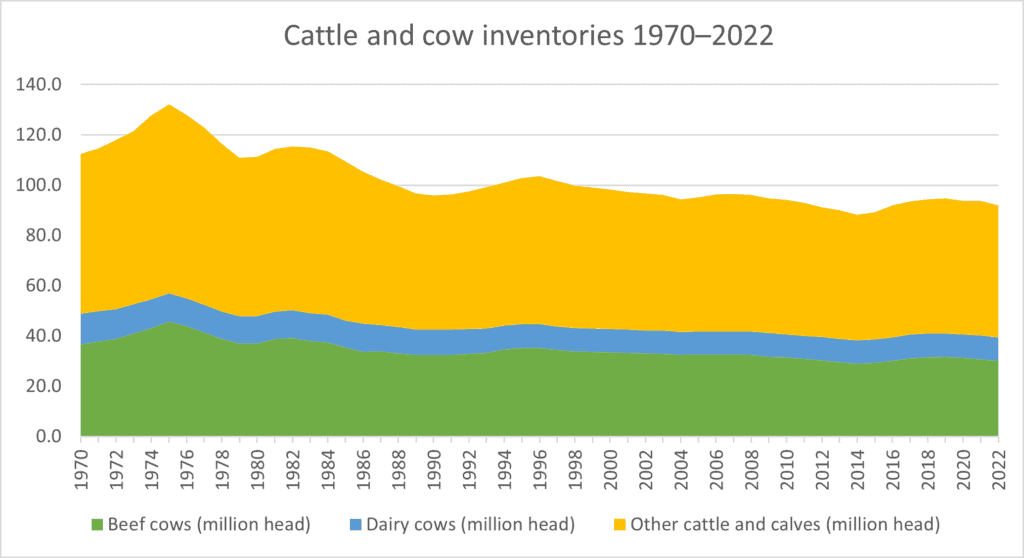
The global cattle herd totals about 1 billion head, including about 95 million raised in the US, according to Statista and USDA. The US cattle ranching industry has approximately 93.8 million cattle and calves as of 2021, continuing consistent with the 2020 value and 91.9 million cattle and calves as of Aug 2022. The United States has two largest beef markets- Japan and South Korea, which accounted for about 47 percent of U.S. exports. The third largest market was China, which accounted for 16 percent of exports. North American beef trade is represented by Mexico and Canada which accounted for 17 percent of total exports.
The second and third largest beef sources OF the United States were Mexico and New Zealand, providing about 20 and 15 percent of U.S. beef imports, respectively. Whereas, Australia is the fourth major supplier, shipping 12 percent of U.S. beef imports. Brazil is the fifth major source that shipped 11 percent of the U.S. beef import needs.
Texas has the most beef cows in the United States in 2021 followed by Oklahoma, Missouri, Nebraska & South Dakota. Texas has more beef cows in 2021 than Missouri and Oklahoma combined. It accounts for roughly 15% of the beef cows in the United States. The top 10 states with the most beef cows account for roughly 59% of the inventory in the United States.
The ranching and livestock industry is expanding more rapidly than any other agricultural sector in the world. The U.S. industry is roughly divided into two production sectors: cow-calf operations and cattle feeding. Cow-calf operations are the backbone of the beef industry in which a herd of cows is kept by a rancher to produce calves for later sale. Cow-calf production is the first stage of the beef production process. An average of about 2.2 years intervenes between breeding a beef cow or heifer to the time their offspring are ready for slaughter.
Cow-calf operations are widespread throughout the United States. there was 91.9 million head of cattle and calves on U.S. farms as of Jan. 1, 2022, according to the Cattle report published by the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS).
Cattle ranching is an important aspect of cow-calf operations and other livestock practices. Livestock raised on ranches is an important part of agriculture. Livestock provides meat for human and animal consumption. They also supply materials, such as leather and wool, for clothing, furniture, and other industries. Ranches also include animals other than livestock such as horses and bulls.
Leading Company
Today, Ranching exists in all the continents except Antarctica. South America has a large ranching culture and the largest meat processing company in the world is JBS S.A.
BRF S.A. is one of the leading food processor companies in Latin America, it was formed through the merger between Sadia and Perdigao in 2013. The company is engaged in producing and distributing fresh and frozen meat products, including beef, turkey, chicken, specialty meats, frozen prepared entrees, and portioned products.
Tyson Foods, Cargill, and Marfrig are also the leading companies in producing and distributing beef products in the market.
Top exporters of beef worldwide
The United States was the largest exporter of beef in the world in 2021 with an export value of 9.3 billion U.S Dollars whereas Brazil with 8 million U.S Dollars. The main reason for the rise was a nearly four times increase in exports to China, growing from just over 100 million pounds in 2020 to over 540 million in 2021. By the end of 2022, Brazil and the United States were forecasted to be the top exporters of beef and veal, with an export volume of 2.6 million and 1.5 million metric tons of beef and veal.
The top four beef exporting countries are Brazil, the United States, India, and Australia. The top four beef exporting countries comprise 60 % of the 2022 projected global total in the USDA report.
Global beef trade is projected to continue expanding to new record levels in 2022. whereas The USA will be the second largest exporting country in the world after Brazil in 2022 with total exports of approximately 58 % of exports from Brazil. While U.S. beef exports are expected to decline in 2022 from the record 2021 levels but will remain at historically high levels.
Forecast- 2023
Global Production is forecasted lower in 2023. U.S. beef production is forecast down 6 percent on tighter cattle inventories. Brazil’s chicken meat exports are forecast up by 1 percent in 2023 on firm demand in key markets and production challenges by key competitors. In 2022, the drought conditions in the United States have resulted in high culling rates and earlier-than-normal placement of cattle in feedlots. This will lead to a smaller cattle herd in 2023. Whereas China’s higher cattle inventories are projected to sustain a 5% increase in beef production and Australian production is expected to rise 13 percent on improved pasture conditions.
Global exports in 2023 are forecasted to shrink by 1 percent due to lower import demand, specifically in China. However, Lower total exports from North America and India can benefit Australia and Brazil. Lowered North American competition in East Asia and rebounding Australian production will allow Australia to boost its shipments and increase its market share. Meanwhile, Brazil’s exports are forecast to record high as aggregate exports from its main competitors (Argentina, Paraguay, Uruguay, and India) are expected to fall 3 percent. Smaller cattle inventories are expected to weigh on the exportable supplies of Argentina, Paraguay, and Uruguay. For India, exports are expected to be unchanged from 2022 with limited growth in several markets.
